HIS-RIS-Modality-PACS coupling: Technology Assessment and future Plan
Hiroshi Kondoh 1), Michihiro Sasagaki 2) , Yoshiharu Sukenobu 2) , Yoshifumi Narumi 2) , Hironobu Nakamura 2) , Yasushi Matsumura 3), Hiroshi Takeda 3), Kiyonari Inamura 4)
1) Dept. of Medical Informatics, Tokushima Univ. Hospital and Dept. of Radiology Osaka Univ. Medical School
2) Dept. of Radiol. Osaka University Hospital
3) Dept. of Medical Infromatics, Osaka University Hospital
4) School of Allied Health Sciences, Faculty of Medicine Osaka Univ.
Abstract
We are making a personal computer (PC)-based hospital-wide HIS-RIS-Modality-PACS coupling. The concept of HIS-RIS-Modality-PACS coupling is flexible, integrated and open system. Each server connects one network and client could access to each server. PACS uses the networks of RIS and HIS. Modalities also get the patient's information from RIS. We started the operation of the system in 1993. The HIS-RIS integrated system covered all of the requests, billing data and reports in the radiological examination, but RIS-Modality communication realized in fourteen computed radiography (CR) systems and one angiography system. PACS was also experimental. It stored images of three CT scanners and eight CRs and delivers to twenty clients in radiology department and ten clients in clinics and wards for about one year with compression.
The technology assessment of the system is important and we had some results of ROC study, time study, character counting in radiological reports, network loading study and questionnaire survey of clinicians' acceptance. These results gave much consideration to make the future plan and we will report the process and the future plan.
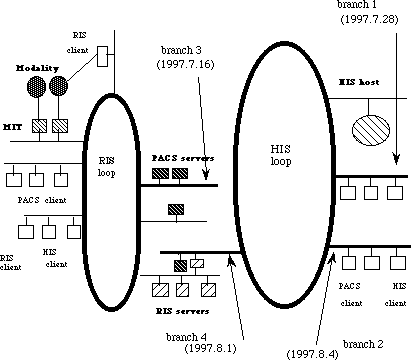
The hospital has 1,076 beds and 2000 outpatients per day. HIS has over 500 PCs as terminals and workstations and main frame, which covers out-patients clinics and wards. RIS has 60 PCs as terminals and five workstations as servers, which covers the department of radiology. Three workstations with three MOD (Magneto-Optical Disk) juke-boxes stored images for over one year (Fig. 1).
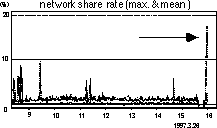
ROC study showed the necessity of high resolution CR for the detection of subtle interstitial abnormality. The data volume of high resolution CR is too large to use in PACS without compression. Therefore PACS was planned for reference image. Time study indicated the decrease of patient waiting time and three times increase of report-making time. (The style was changed from handwriting to keyboard) The availability and high speed database will make us to accept the system. Image display time decreased from 30 to 5 seconds in five years. LAN analyzer recorded the network share rate for a day to indicate the network loads. Image transport was not so frequent in this clinical trial because the radiographs distribution system was also working. We simultaneously forced several terminals to retrieve many images at the same branch LAN. These peaks did not reach 20% even if three terminal retrieve images at the same time in the HIS branch LAN (Fig.2), but it reached easily 20 % in the branch connecting to servers. Intermediate servers seemed to be necessary for image delivery to clinics and wards. Clinicians' opinion was recorded on a 5-point scale for image quality, response, and function. The image quality is almost acceptable as reference especially in CT, but the response and operations get lower scores and should be improved. They want to add MRI and RI in PACS in the next. Expansion of PACS seemed to be important even if it is for references.
 |
 |
| Fig.1 Network of HIS-RIS-Modality-PACS coupling | Fig. 2 Network share rate of HIS branch for clients |
Oral presentation at EuroPACS'98, Barcelona, Spain